LASMA-LR Instrument Portrait
The LASMA-LR instrument is almost a duplication of the LASMA instrument used on the Phobos-Grunt spacecraft. The Phobos-Grunt mission unfortunately failed and was lost.
The instrument is characterized in its appearance by
- - its small dimensions of only130 × 206 × 254 mm
- - the low weight of 2.8 kg and
- - the low mean operating power consumption of only 8 W.
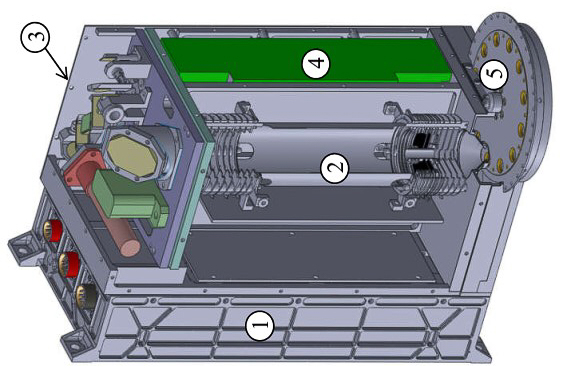
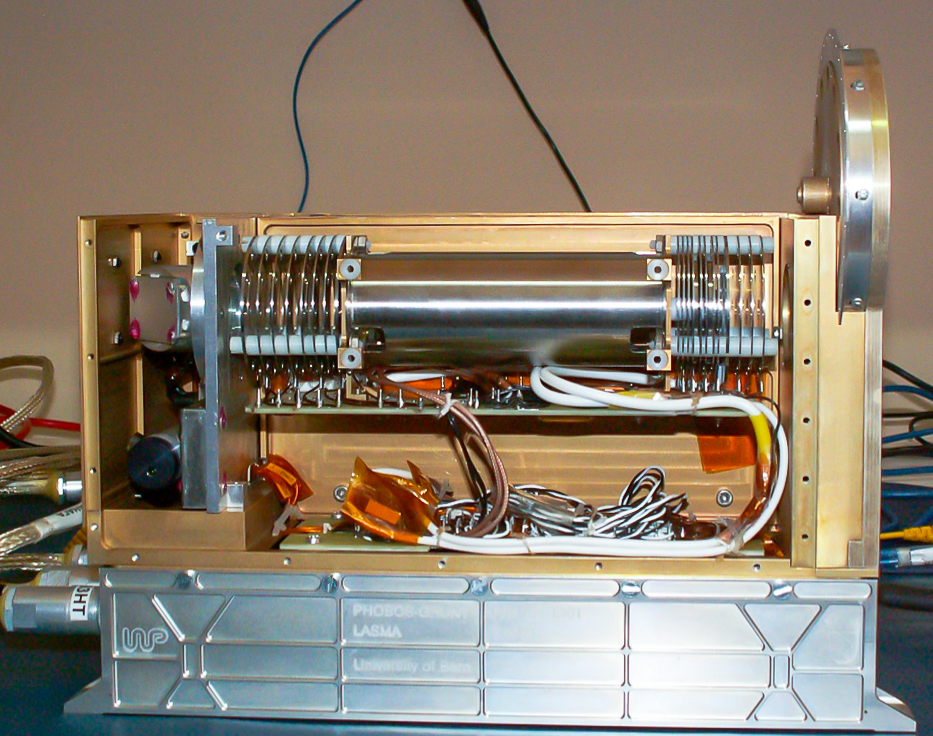
As its predecessor, structurally, the LASMA-LR instrument is in the form of a single unit, see picture LASMA-LR construction below. It features the following main units:
- the electronics module (University of Bern, Switzerland),
- the mass analyzer (Space Research Institute of RAS, Russia)
- the laser optical module (POLYUS Research Institute of M.F. Stelmakh Joint Stock Company (Russia)
- the power supply and control unit for the laser emitter and
- the sample receiving device (both Space Research Institute of RAS, Russia)
How the LASMA-LR mass spectrometer works
The instrument is able to perform analysis of element and isotope composition of solid samples (regolith and dust) It can accommodate up to 12 soil samples for detailed chemical analysis with high accuracy and high spatial resolution. The soil samples are delivered to the LASMA-LR by an articulated arm from the spacecraft. Even the analysis of single grains of lunar regolith will be possible with the LASMA-LR!
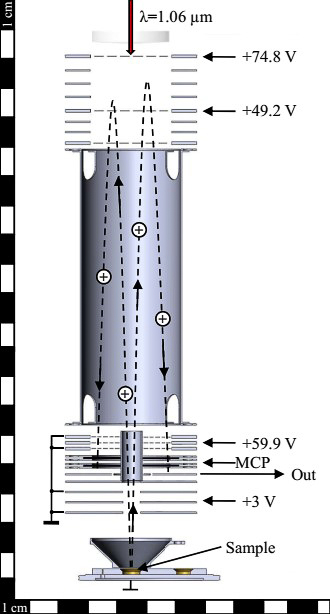
The principle of the instrument operation consists in the complete atomization and ionization of the substance removed from the sample by an intense laser pulse. The Laser irradiation will be optimised either for elemental and isotopic analysis (ablation mode analysis) or to chemical analysis (desorption mode analysis).
After the irradiated material is released from the sample, the process is followed by the separation of the ions during their free expansion in the drift path of the time of flight analyzer as a function of their mass and charge. Subsequently, this allows the registration of the time of flight of the ions from the sample to the detector. Ions with different masses have different velocities according to their mass. In fact, ions with a lower mass are faster than more massive ones, thus they have a shorter traveling time along the drift path and arrive earlier at the detector.
Publications
- Chumikov-et-al_Design,Charachteristics-Scientific-Tasks-of-LASMA-LR-MS-onboard-Luna-25-and-Luna-27.pdf (PDF, 138KB)
- Managadze-et- al-2010_Study-of-the-main-geochemical-characteristics-of-Phobos'Regolih.pdf (PDF, 151KB)
- Wurz et al-Laser Mass Spectrometry in Planetary Science (PDF, 135KB)
- Iakovleva_Inauguraldissertation-2011.12.21 (PDF, 11.9 MB)
